3D Printing in Education: Current Use and Benefits
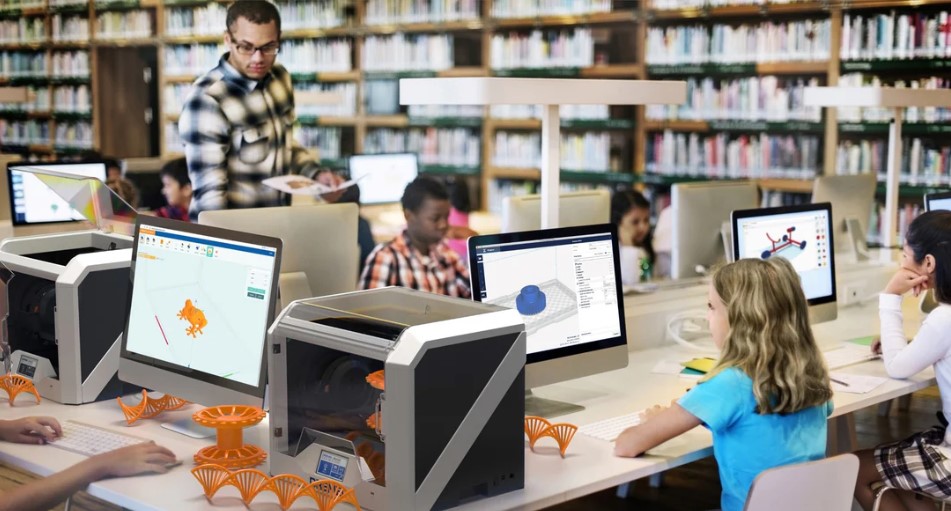
3D printing is being integrated into classrooms and labs across the globe, enhancing traditional learning methods with hands-on experiences. This technology allows students to transform theoretical knowledge into tangible objects, bridging the gap between abstract concepts and practical applications.
Here are some of the key benefits of using 3D printing in education:
1. Enhancing Creativity and Innovation
3D printing provides students with the freedom to bring their ideas to life. Whether they’re designing a model of the solar system, building prototypes of machines, or creating artistic sculptures, 3D printing encourages creative expression and innovation. Students are no longer limited to pen-and-paper sketches—they can now create real, functioning models that enhance their understanding and fuel their creativity.
2. Hands-On Learning
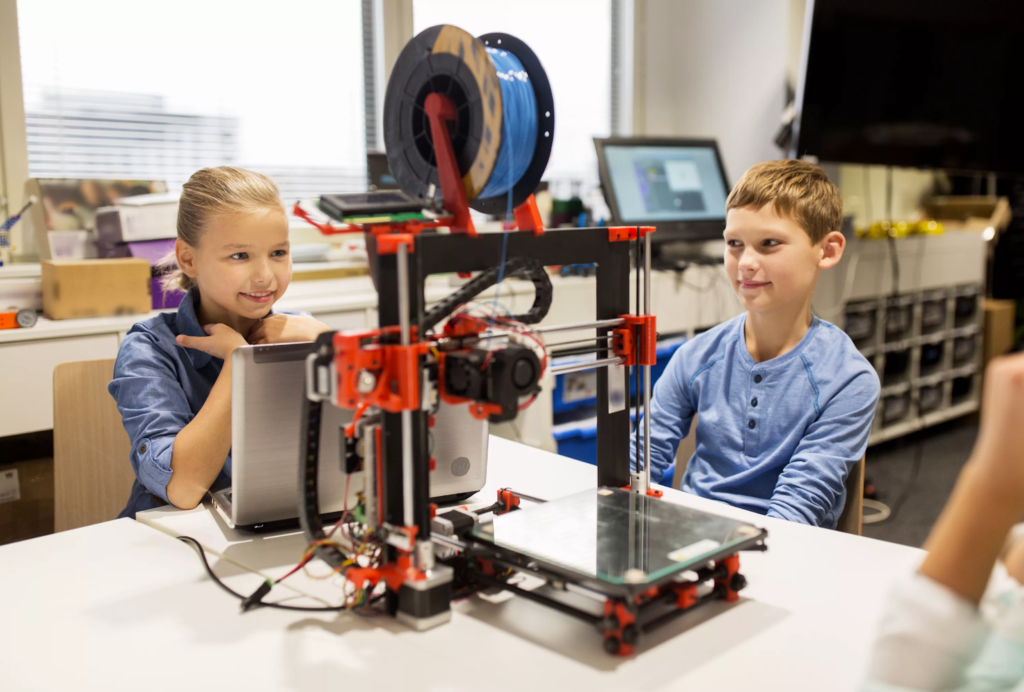
Incorporating 3D printing into the curriculum enables hands-on learning across a wide range of subjects. In subjects like engineering, architecture, and biology, students can print complex structures such as bridges, buildings, or anatomical models, allowing them to see and interact with the concepts they are studying. This hands-on approach is more engaging than traditional learning methods and helps students retain knowledge more effectively.
3. Improving Problem-Solving Skills
With 3D printing, students are encouraged to think critically and experiment. They can create multiple versions of their designs, test prototypes, and refine their work based on the results. The iterative nature of 3D printing helps students learn from their failures and improve their problem-solving skills. For example, in engineering courses, students can design mechanical parts, test their functionality, and modify their designs until they achieve the desired outcome.
4. Encouraging Collaboration
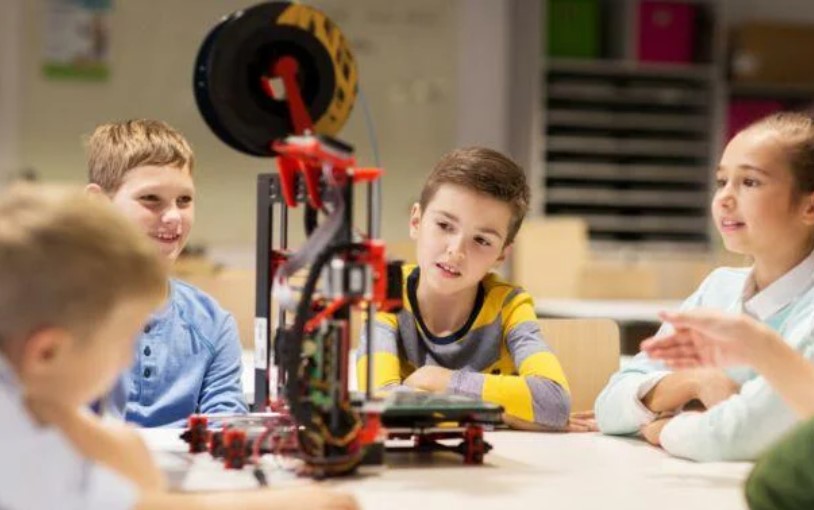
3D printing fosters collaboration by encouraging students to work together on projects. Whether they’re designing a robot, creating a 3D-printed model of a city, or working on an art installation, students can collaborate on different aspects of a project, combining their skills and ideas to create something meaningful. This collaborative approach also mirrors real-world professional environments, where teamwork and interdisciplinary knowledge are essential.
5. Making Abstract Concepts Tangible
In fields like mathematics and physics, abstract concepts can be difficult for students to grasp. With 3D printing, students can visualize and interact with these concepts in ways that traditional teaching methods cannot offer. For instance, students can print geometric shapes or molecular models to better understand mathematical formulas and chemical structures. This makes abstract concepts more accessible and easier to comprehend.
Opportunities for 3D Printing in Education and Training
The integration of 3D printing in education offers a multitude of opportunities to enhance learning experiences, broaden career paths, and inspire future innovators. As the technology continues to advance, it is expected to create new opportunities for students, teachers, and educational institutions. Here are some of the major opportunities that lie ahead:
1. STEM Education
STEM education is one of the primary beneficiaries of 3D printing. In STEM fields—science, technology, engineering, and mathematics—3D printing allows students to create physical models of scientific phenomena, prototypes for engineering projects, and tools for experimentation. For example, students studying biology can print 3D models of cells or organs, while engineering students can create functional prototypes of machines or devices.
As the demand for skilled professionals in STEM industries grows, 3D printing will play a crucial role in preparing students for future careers in these fields. By introducing them to cutting-edge technologies and enabling hands-on experimentation, 3D printing fosters the skills and knowledge needed for tomorrow’s workforce.
2. Design and Engineering Training
For students in design, architecture, and engineering programs, 3D printing is an invaluable tool for training and skill development. Future architects can create 3D models of buildings and urban designs, while engineers can print mechanical parts and systems to test and refine their designs. This real-world experience prepares students for careers in design and engineering, giving them a competitive edge in the job market.
As more industries adopt 3D printing, the demand for professionals with expertise in this technology will continue to grow. Educational institutions that integrate 3D printing into their curricula will be better equipped to produce graduates who are ready to enter the workforce with the skills needed to succeed.
3. Medical and Healthcare Education
In medical and healthcare education, 3D printing is transforming the way students learn anatomy, surgery, and medical device design. Medical students can print 3D models of human organs for dissection and study, allowing them to gain a deeper understanding of anatomy. Surgeons can practice complex procedures using 3D-printed models, improving their skills and reducing the risk of errors during actual surgeries.
As bioprinting technology advances, healthcare training will also evolve. In the future, medical students may use 3D printers to create living tissues and organs for research and experimentation, further revolutionizing medical education.