Why EBM is Gaining Traction
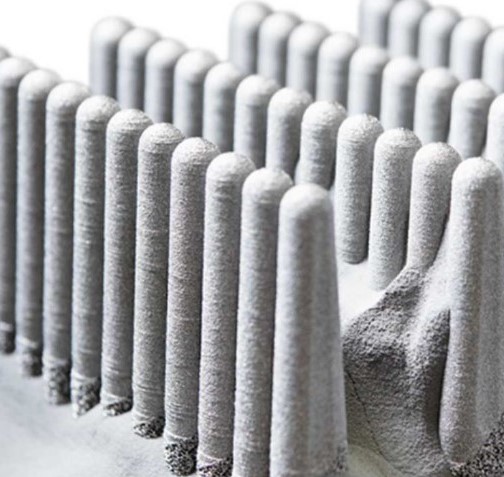
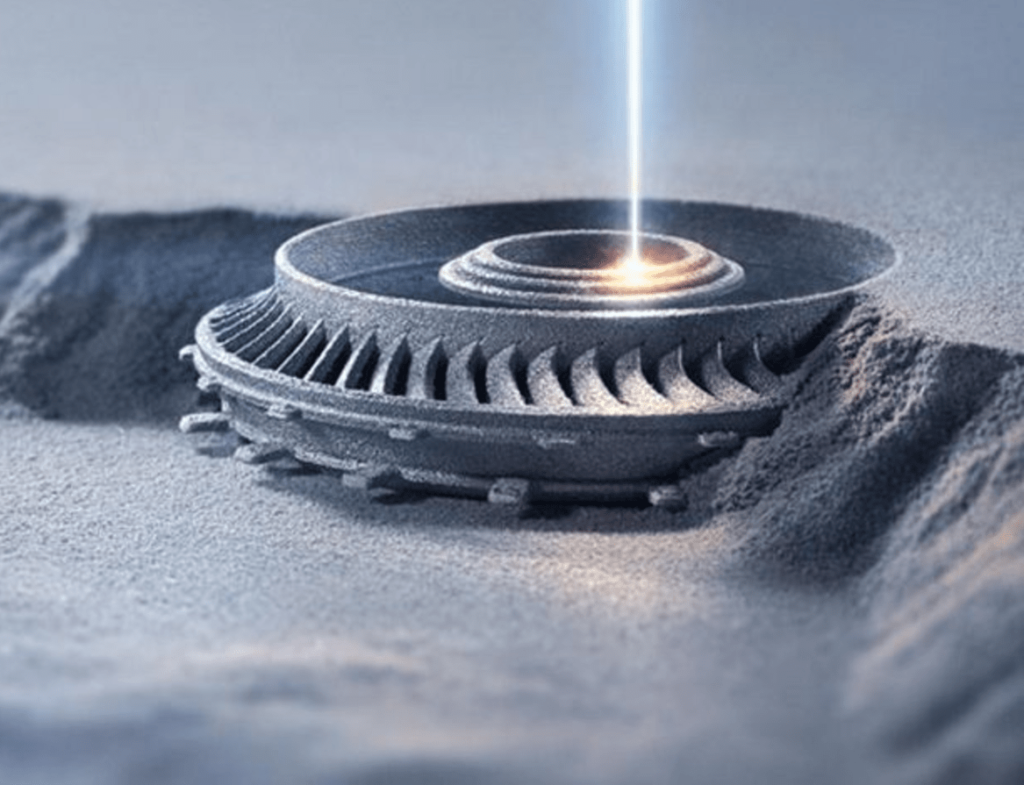
EBM is particularly well-suited for industries that require materials with exceptional mechanical properties and biocompatibility. For instance, titanium—one of the primary materials used in EBM—is not only strong and lightweight but also biocompatible, making it ideal for medical implants and aerospace components. Despite some limitations, such as lower accuracy and a granular finish, EBM offers significant advantages, particularly in applications where speed and material properties are more critical than precision.
Key Industries Benefiting from EBM Technology
1. Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry is a natural fit for EBM technology due to its need for lightweight yet strong components. Titanium’s strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosion make it an excellent choice for aerospace applications. EBM is used to produce various aircraft components, including engine parts, brackets, and structural elements. The ability to rapidly produce complex shapes with minimal waste is a significant advantage in this industry, where innovation and efficiency are crucial.
2. Medical Industry
In the medical field, EBM is transforming the production of implants and prosthetics. The biocompatibility of titanium ensures that it is well-tolerated by the human body, reducing the risk of rejection and complications. EBM allows for the creation of patient-specific implants, such as dental implants, hip and knee replacements, and spinal devices, which are tailored to the individual’s anatomy. This level of customization, combined with the mechanical strength of titanium, results in implants that are not only functional but also long-lasting.
3. Automotive Industry
EBM is also making strides in the automotive industry, where the demand for lightweight and durable components is ever-present. High-performance vehicles, including sports cars and luxury models, benefit from the precision and material strength offered by EBM. Components such as engine parts, transmission components, and even custom-designed aesthetic elements can be produced using EBM, helping manufacturers reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency without compromising on strength or durability.
4. Defense Industry
The defense sector, with its rigorous demands for high-performance materials and components, is another area where EBM is making an impact. The ability to produce parts with complex geometries and tailored properties makes EBM ideal for manufacturing military-grade components. These include parts for aircraft, naval vessels, and ground vehicles that require the utmost reliability and performance under extreme conditions. The speed and flexibility of EBM also allow for rapid prototyping and production, which is vital in a sector where technological advancements are constantly evolving.
Balancing Speed with Precision: The EBM Trade-Off
While EBM offers impressive speed and the ability to work with advanced materials, it does have some limitations. The technology is known for producing parts with a granular finish and lower dimensional accuracy compared to other additive manufacturing techniques, such as laser sintering. As a result, EBM is more suited to applications where these factors are less critical. However, for industries where rapid production and material properties are paramount, the benefits of EBM far outweigh these drawbacks.