How Does Binder Jetting Work?
Binder Jetting is a multi-step process that methodically builds 3D objects layer by layer. Here’s a detailed look at how it works:
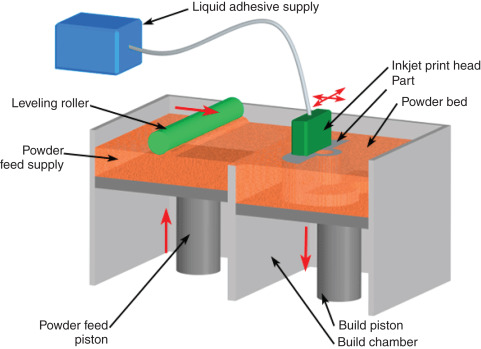
1. Powder Spreading
The process begins with powder spreading. A roller or blade spreads a thin, even layer of powder material over the build platform. This powder can be composed of various materials, including metals (like stainless steel or titanium), ceramics, sand, or even polymers. The choice of powder depends on the final application of the printed object.
2. Binder Deposition
Next, the binder deposition step takes place. An inkjet print head moves precisely over the powder bed, depositing tiny droplets of a liquid bonding agent, or binder, at specific locations where the object will be formed. The binder acts like a glue, selectively adhering the powder particles together in the areas defined by the digital model of the part.
3. Layer Bonding and Solidification
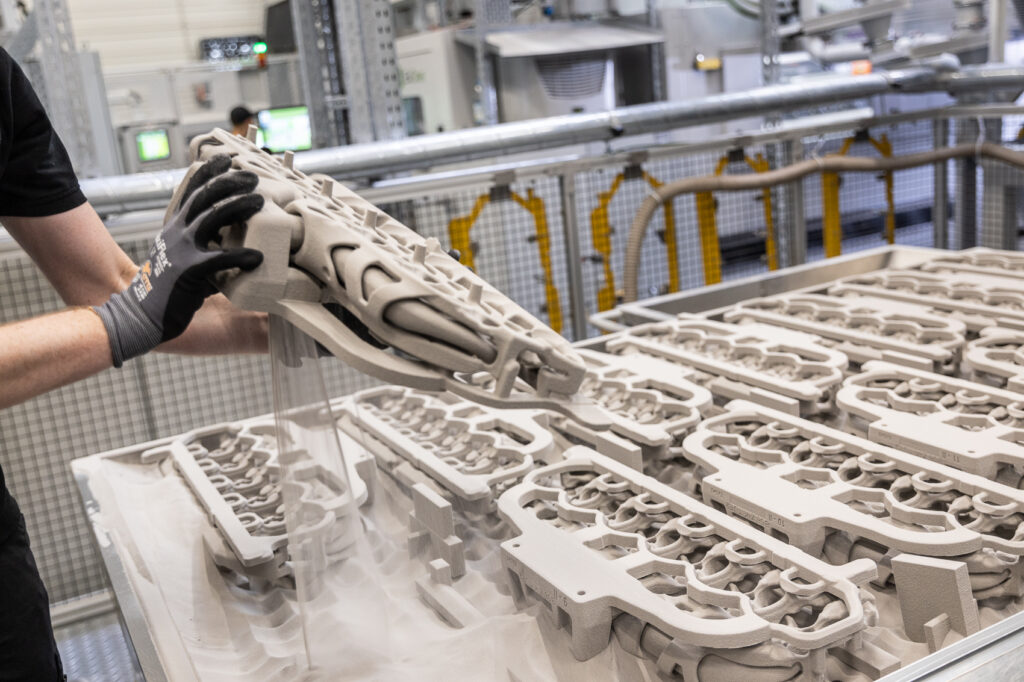
As the binder is deposited, it bonds the powder particles together in the designated areas, creating a solid layer of the part. The unbonded powder remains loose and can be reused later, making this process material-efficient.
4. Lower Powder Bed and Repeat
After one layer is complete, the build platform is lowered slightly to accommodate the next layer of powder. Another thin layer of powder is spread over the platform, and the binder deposition process repeats. This layering process continues until the entire part is formed, with each new layer bonding to the one below it.
5. Curing and Sintering
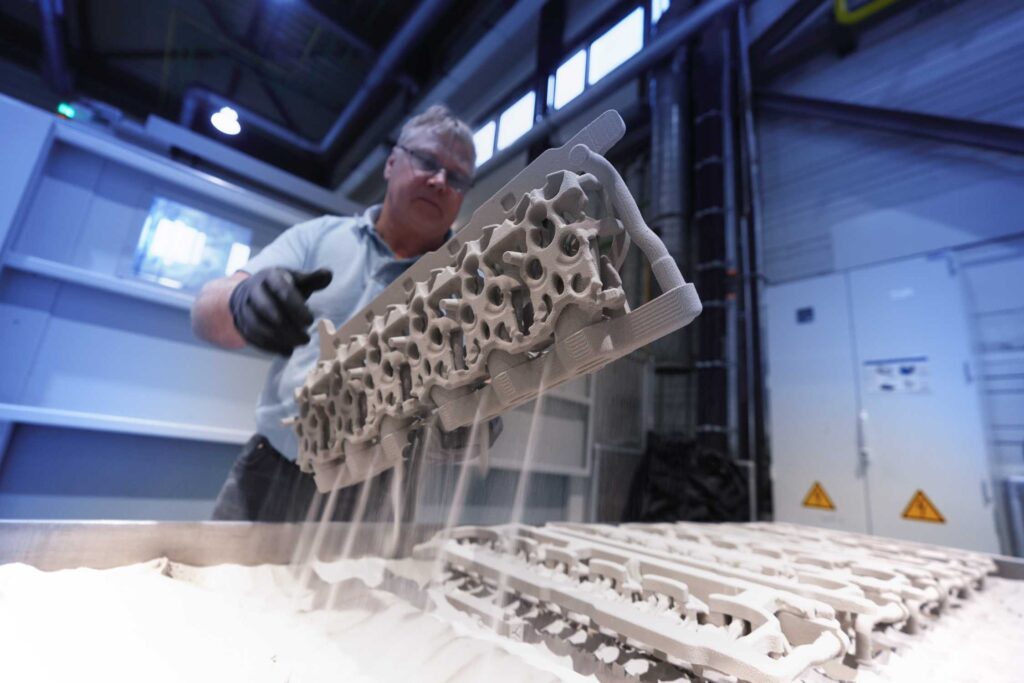
Once the printing process is complete, the object, known as a “green part,” requires further processing. The green part undergoes curing to harden the binder and ensure the part’s stability. Any excess powder surrounding the part is carefully removed and can often be recycled for future use.
For metal parts, an additional sintering step is usually required. Sintering involves heating the part to just below its melting point to increase its strength and density, making it suitable for functional use.
Primary Uses of Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting offers several advantages, making it suitable for a variety of applications across different industries. Some of its primary uses include:
1. Prototyping
Binder Jetting is widely used for creating prototypes due to its ability to produce detailed parts quickly and affordably. The process is particularly advantageous for producing large, complex prototypes that would be difficult or expensive to make with other methods.
2. Metal Parts Production
In the manufacturing industry, Binder Jetting is often used to produce metal parts, especially in cases where traditional casting methods would be too slow or costly. After printing and sintering, the metal parts can exhibit mechanical properties comparable to those produced by conventional methods, making them suitable for functional applications.
3. Sand Casting Molds and Cores
One of the most common uses of Binder Jetting is in the production of sand casting molds and cores. The technology allows for the rapid creation of complex sand molds, reducing lead times and costs compared to traditional mold-making methods.
4. Ceramic Components
Binder Jetting is also employed in the production of ceramic components, including those used in aerospace, automotive, and medical applications. The process can produce intricate ceramic parts that are difficult to create using traditional ceramic manufacturing techniques.
5. Architectural Models and Art
The ability of Binder Jetting to create highly detailed and complex structures makes it ideal for producing architectural models and artistic sculptures. Artists and architects can take advantage of the technology to bring intricate designs to life that would be nearly impossible to craft by hand.