The Mediterranean Diet: Overview and Benefits
What is the Mediterranean Diet?
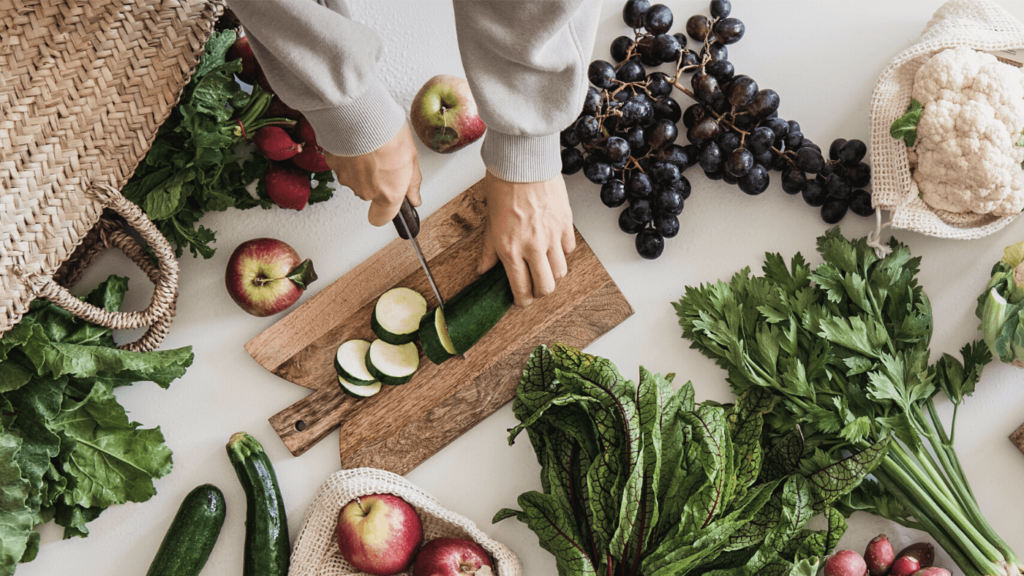
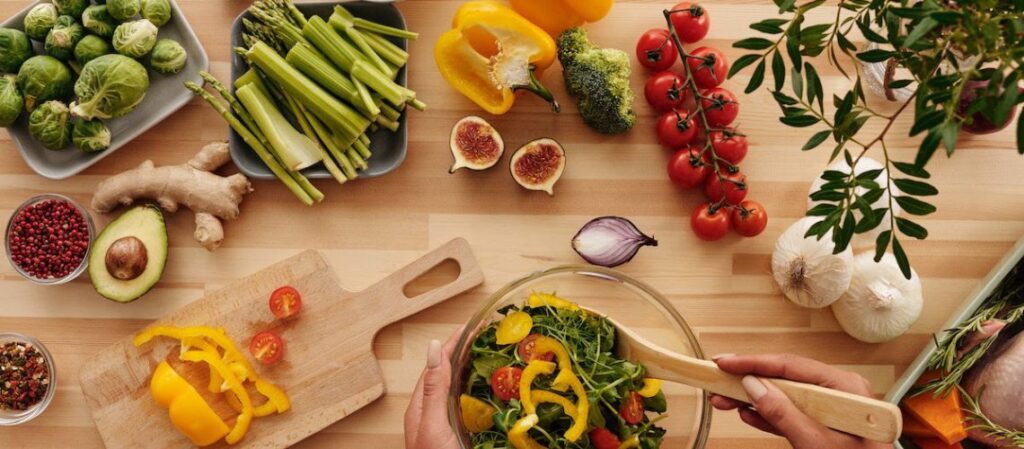
The Mediterranean diet is inspired by the traditional eating patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, including France, Spain, Greece, and Italy. It emphasizes:
- Fruits and vegetables: A variety of colorful and nutrient-dense options.
- Whole grains: Including oats, brown rice, and whole wheat products.
- Legumes: Beans, peas, lentils, and chickpeas.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, sunflower seeds, and more.
- Healthy fats: Primarily from extra virgin olive oil and avocados.
- Fish and seafood: Consumed at least twice a week.
- Moderate dairy: Cheese and yogurt in moderation.
- Poultry and eggs: Consumed in moderate amounts.
- Herbs and spices: Used to flavor food instead of salt.
Plant based, not meat based
The foundation of the Mediterranean diet is plant foods. That means meals are built around vegetables, fruits, herbs, nuts, beans and whole grains.
Moderate amounts of dairy, poultry and eggs are part of the Mediterranean diet, as is seafood. In contrast, red meat is eaten only once in a while.
Healthy fats
Unsaturated fats are a strength of the Mediterranean diet. They’re eaten instead of saturated and trans fats, which play roles in heart disease.
Olive oil and nuts are the main sources of fat in the Mediterranean diet. They provide unsaturated fat. When unsaturated fat comes from plant sources, it seems to lower levels of total cholesterol as well as low-density lipoprotein, also called LDL or “bad” cholesterol.
Replacing saturated fat with polyunsaturated fat lowers risk of cardiovascular disease events and death related to cardiovascular disease, according to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
Seafood, seeds, nuts, legumes and some vegetable oils have healthy fats, including the polyunsaturated kind.
Fish also are a key part of the Mediterranean diet. Some healthy choices are:
- Mackerel.
- Herring.
- Sardines.
- Albacore tuna.
- Salmon.
- Anchovies.
These are known as fatty fish. And the fats they contain are omega-3 fatty acids.
Omega-3s are unsaturated fats that may lower immune system action in the body known as inflammation. They also may help reduce blood fats called triglycerides, and they affect blood clotting. Omega 3s may lower the risk of stroke and heart failure too.
Lean fish and shellfish also are included in the Mediterranean diet. Shellfish include shrimp, crab, clams and scallops. Some types of lean fish are cod, haddock, hake and whitefish.
Choose fish that are low in mercury, such as the ones listed above. This is important for children ages 1 to 11 and people who are pregnant and breastfeeding.
Too much mercury can harm the brain and nervous system over time. If your family catches and eats fish, check local fish advisories to find out about any cases of mercury contamination.