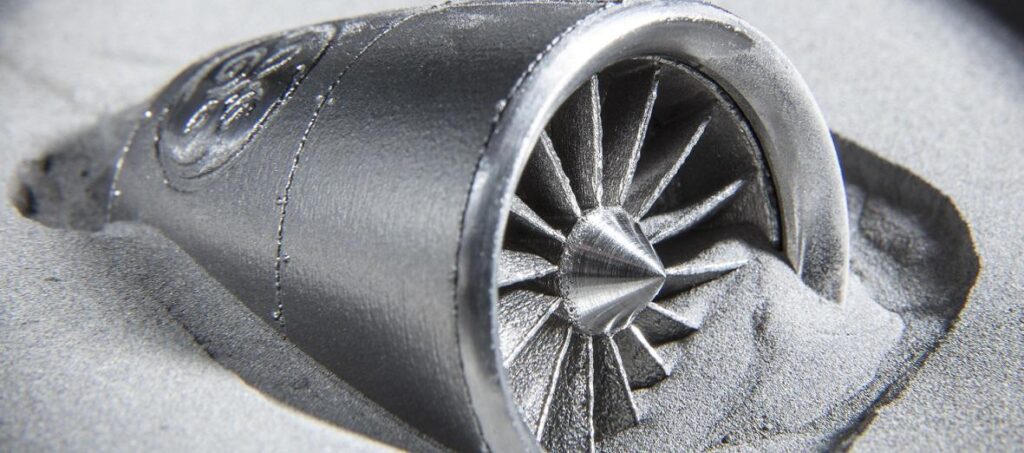
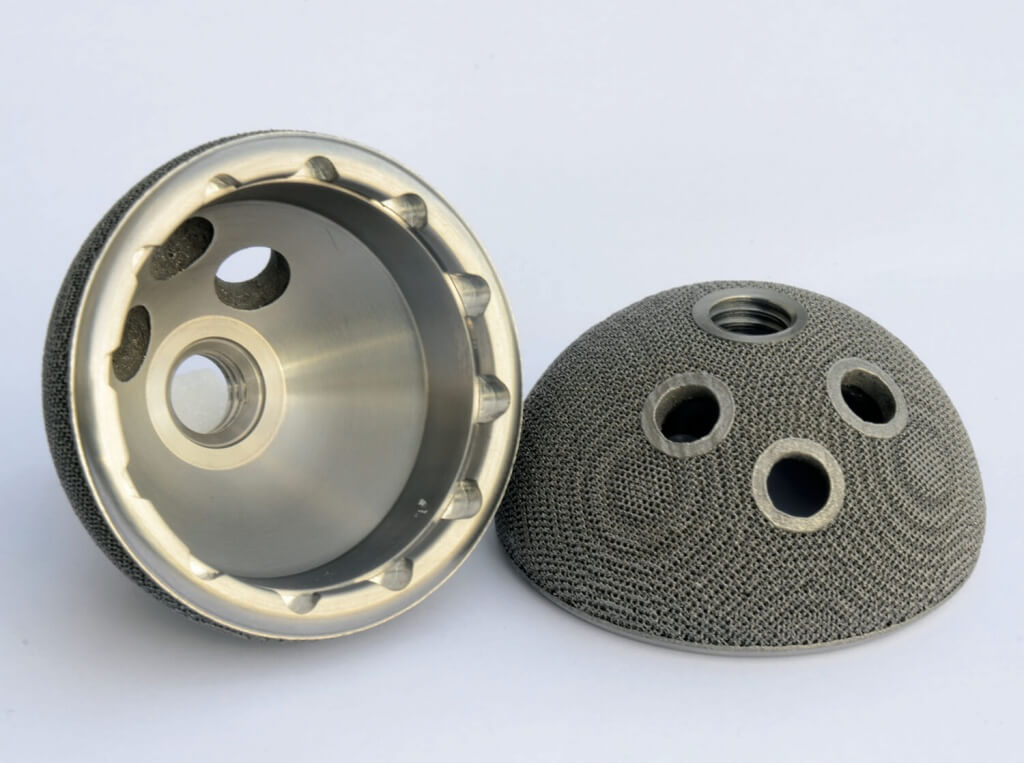
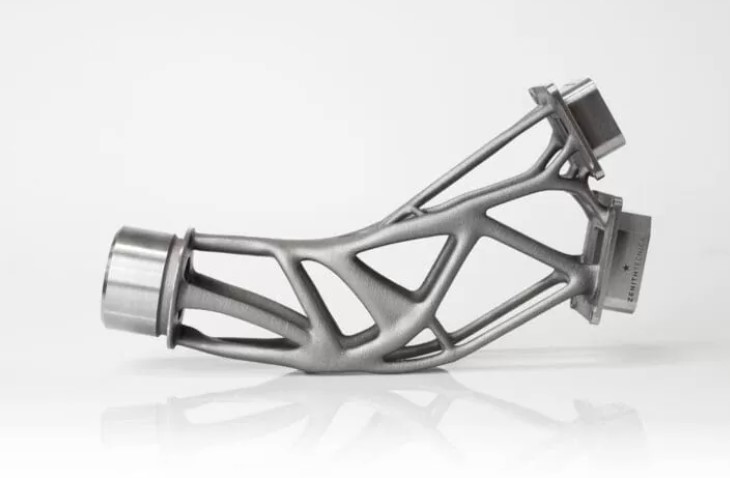
The Working Process of EBM
EBM operates on the principles of powder bed fusion, a method common to several additive manufacturing technologies. However, what sets EBM apart is its use of an electron beam rather than a laser to melt and fuse metal powder. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the EBM process works:
1. Electron Beam Generation
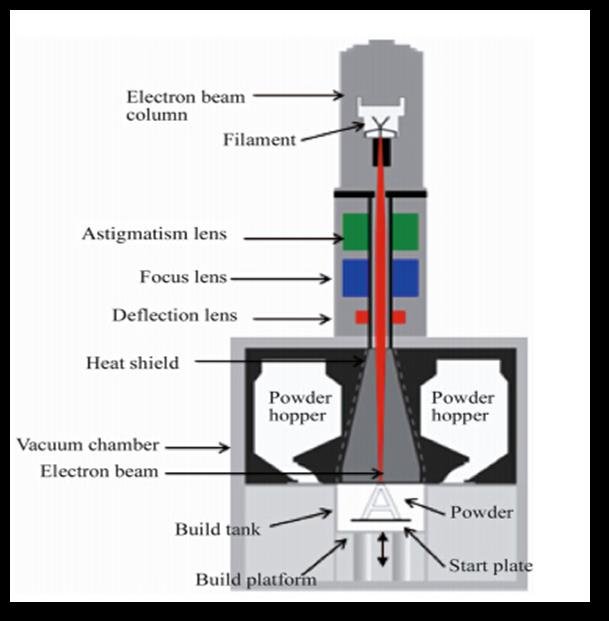
At the heart of the EBM process is the electron gun, which is a key component that produces the electron beam used for melting the metal powder. The gun consists of a tungsten filament, which is superheated to emit a stream of electrons. These electrons are accelerated to roughly half the speed of light within a vacuum chamber, where they are directed onto the build platform by a magnetic field.
2. Powder Layer Deposition
Similar to other powder bed fusion processes, EBM starts by spreading a thin layer of metal powder across the build platform. The powder bed typically consists of electrically conductive materials, which are essential for the electron beam to interact with and melt the material effectively.
3. Melting and Fusing the Powder
The electron beam, guided by a magnetic field, is then directed to specific locations on the powder bed as dictated by a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model. The high-energy electrons strike the metal powder, generating heat through kinetic energy, which melts the powder and fuses it into a solid layer. This process is repeated layer by layer, with each new layer bonding to the one beneath it, gradually building up the entire 3D object.
4. Vacuum Environment
One of the unique aspects of EBM is that it operates within a vacuum chamber. This environment is crucial for two main reasons:
- Prevents Oxidation: Treating metals at high temperatures increases the risk of oxidation, which can lead to defects such as brittleness in the final product. The vacuum chamber eliminates oxygen, allowing for higher processing temperatures without the risk of oxidation.
- Relieves Internal Stresses: The vacuum environment also helps in relieving internal stresses within the metal during the melting process, resulting in more resilient and flexible parts.
5. Final Part Removal and Post-Processing
Once the printing is complete, the part is allowed to cool within the vacuum chamber before it is removed. The surrounding loose powder is then brushed away, and the part may undergo additional post-processing steps such as heat treatment or machining to achieve the desired properties and finish.
Materials Used in EBM Printing
EBM is specifically designed for electrically conductive materials, which can withstand the high temperatures generated by the electron beam. As a result, it is predominantly used with metals, particularly those with high melting points. The main materials used in EBM include:
- Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Titanium and its alloys are among the most common materials used in EBM. These materials are highly valued for their strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive, and medical applications.
- Chromium-Cobalt Alloys: These alloys are also frequently used in EBM due to their strength and wear resistance. Chromium-cobalt is often used in medical implants and dental applications where durability and biocompatibility are essential.
While EBM excels with these metals, it is not suitable for ceramics or polymers. The reason for this limitation lies in the process itself—EBM relies on electrical charges and extremely high temperatures to melt materials. Since ceramics and polymers are not electrically conductive and cannot withstand the extreme temperatures required, they are incompatible with this technology.