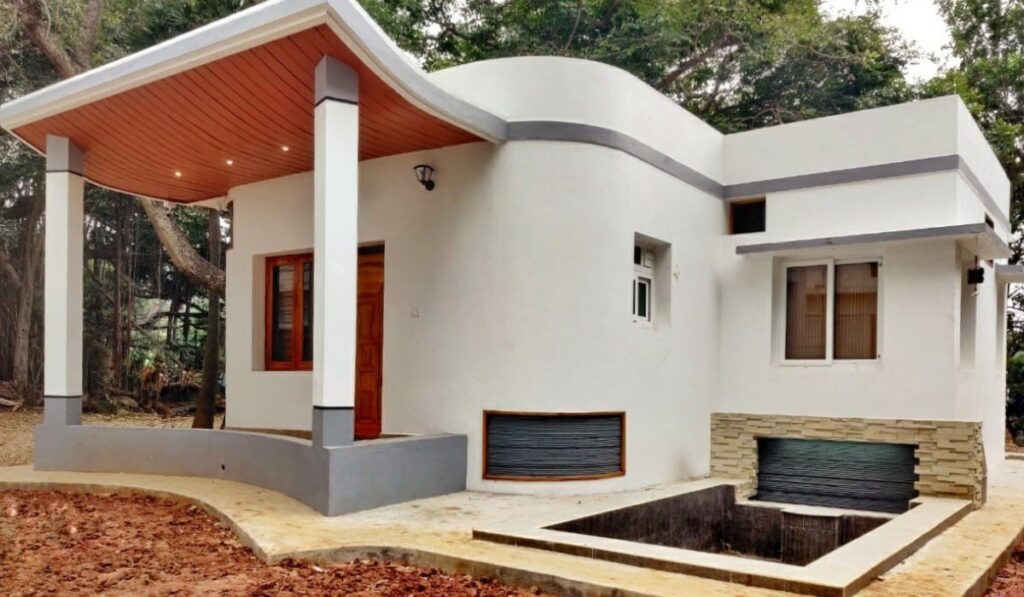
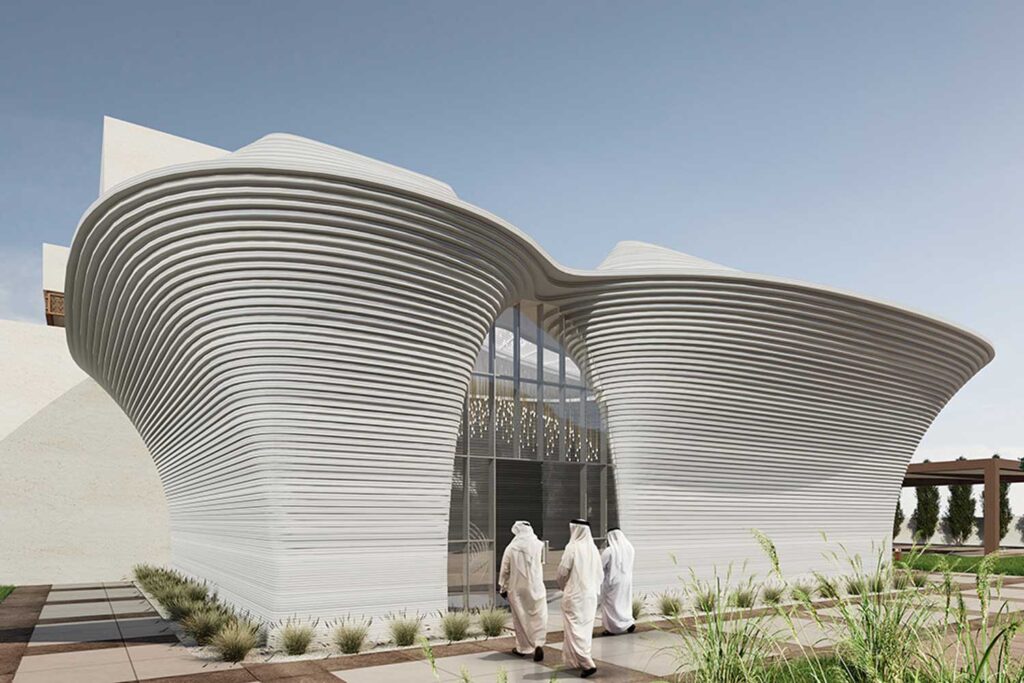
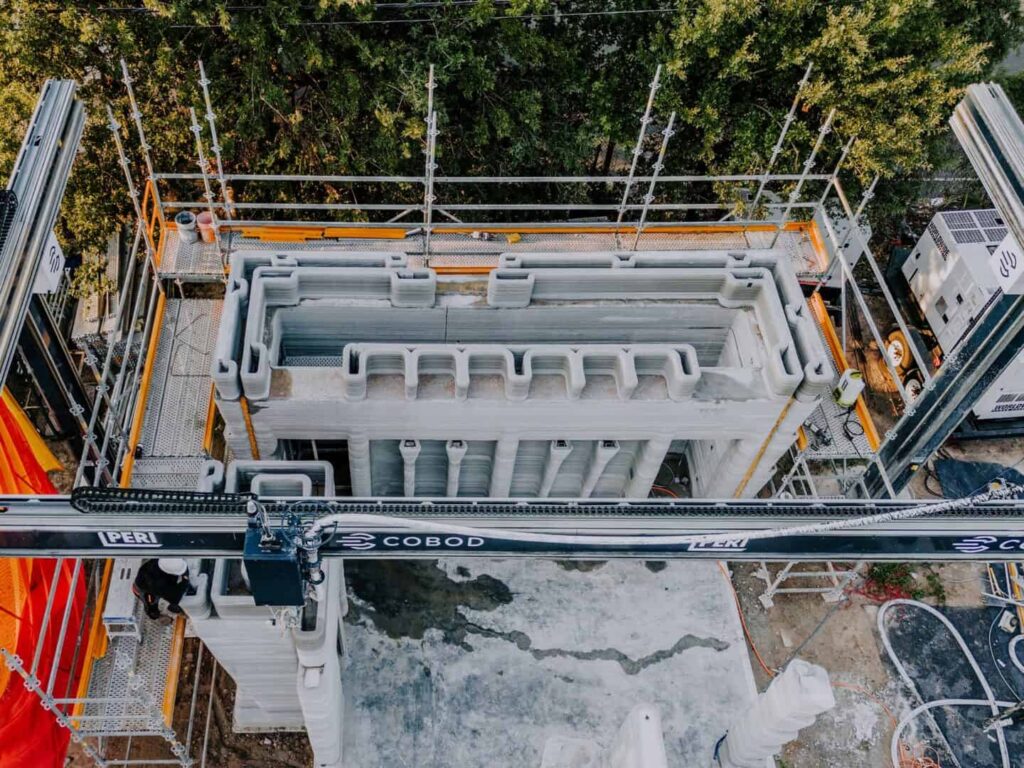
How 3D Printing Contributes to Sustainability
3D printing operates on a fundamentally different model than traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which often involve cutting away material to create a final product. Instead, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer directly from digital models. This method offers several sustainability benefits:
1. Reduced Material Waste
Traditional manufacturing processes can generate significant amounts of waste, as excess material is often discarded during production. In contrast, 3D printing utilizes only the material necessary to create the object, which minimizes waste. For instance, in additive manufacturing, support structures can be designed to use minimal material, and any unused filament can often be recycled for future prints.
2. Energy Efficiency
3D printing is generally more energy-efficient than traditional manufacturing methods. By directly constructing objects from digital designs, it reduces the energy-intensive processes of machining, molding, and assembly. Moreover, certain 3D printing technologies can operate at lower temperatures, further decreasing energy consumption. This efficiency contributes to the overall carbon footprint reduction of the manufacturing process.
3. Localized Production
3D printing enables on-demand and localized production, which can significantly reduce transportation-related emissions. By producing goods closer to their point of use, companies can minimize the energy and resources involved in shipping products over long distances. This localized approach not only cuts down on carbon emissions but also enhances supply chain resilience.
4. Sustainable Materials
The rise of bioplastics and other sustainable materials for 3D printing opens new avenues for environmentally friendly production. Many 3D printing materials can be sourced from renewable resources, such as plant-based plastics, which further reduces reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, some companies are exploring the use of recycled materials in 3D printing processes, further enhancing sustainability.
Environmental Impact of 3D Printing
The environmental impact of 3D printing can be multifaceted, encompassing both positive contributions to sustainability and potential drawbacks. Here’s a closer look at the implications:
Positive Environmental Impact
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: The combination of reduced waste and energy efficiency can lead to a lower overall carbon footprint for products manufactured using 3D printing.
- Resource Conservation: By utilizing only the necessary material and enabling the use of recycled materials, 3D printing helps conserve natural resources and promote circular economy practices.
- Innovative Designs for Sustainability: 3D printing allows for complex geometries and designs that can enhance product performance while using fewer materials, such as lightweight structures in aerospace and automotive applications.
Negative Environmental Impact
- Energy Source Dependency: While 3D printing is generally energy-efficient, the environmental benefits can be undermined if the electricity used comes from non-renewable sources. Transitioning to renewable energy sources is essential to maximize sustainability.
- Material Production Impact: The production of 3D printing materials, especially conventional plastics, can have negative environmental impacts if not sourced responsibly. It’s crucial to focus on sustainable material sourcing to mitigate these effects.
Pros and Cons of 3D Printing
Pros
- Waste Reduction: Utilizes only necessary materials, leading to less waste.
- Energy Efficiency: Generally requires less energy than traditional manufacturing.
- Customization: Enables tailored designs that can meet specific needs without excess material.
- Rapid Prototyping: Speeds up the design process, allowing for faster iteration and innovation.
- Localized Production: Reduces transportation emissions by enabling local manufacturing.
Cons
- Material Limitations: Not all materials are suitable for 3D printing, and some may not have the desired properties.
- Initial Costs: While prices for 3D printers are decreasing, high-quality machines can still be expensive.
- Quality Control: Achieving consistent quality across multiple prints can be challenging, especially with varying materials.
- Environmental Trade-offs: Some 3D printing materials can have a negative environmental impact if not managed properly.
Challenges Facing 3D Printing and Sustainability
While the potential of 3D printing to contribute to a sustainable future is significant, several challenges must be addressed:
1. Material Sustainability
Finding and developing sustainable materials for 3D printing is crucial. The industry must focus on creating biodegradable and recyclable options that can minimize the environmental impact of the materials used.
2. Energy Dependency
To fully harness the sustainability benefits of 3D printing, it is essential to transition to renewable energy sources. Manufacturers must consider the entire lifecycle of energy use in the production process.
3. Regulatory Frameworks
As 3D printing technology advances, regulatory frameworks must evolve to address safety, environmental, and quality standards. Establishing guidelines will be essential for sustainable practices in the industry.
4. Scaling Up
While 3D printing is beneficial for small-scale production, scaling up to meet larger manufacturing demands while maintaining sustainability is a challenge. Finding ways to effectively integrate 3D printing into existing manufacturing ecosystems will be crucial.