SLA working process and what materials used ?
Stereolithography (SLA) is one of the earliest and most influential forms of 3D printing technology, known for producing high-resolution, detailed parts using light-reactive materials. This blog will explore the history of SLA, how it works, and the range of materials it uses, providing a comprehensive overview of this fascinating technology.
The History of SLA 3D Printing
SLA 3D printing traces its origins back to the early 1980s when Japanese researcher Dr. Hideo Kodama first developed a modern layered approach to stereolithography. He used ultraviolet (UV) light to cure photosensitive polymers, laying the groundwork for the technology we know today.
The term “stereolithography” was later coined by Charles (Chuck) W. Hull, who patented the technology in 1986 and went on to found 3D Systems to commercialize it. Hull’s method involved creating 3D objects by successively “printing” thin layers of material curable by ultraviolet light. The initial SLA 3D printers were large, industrial machines, often costing over $100,000, and required complex infrastructure and maintenance.
What is SLA 3D Printing?
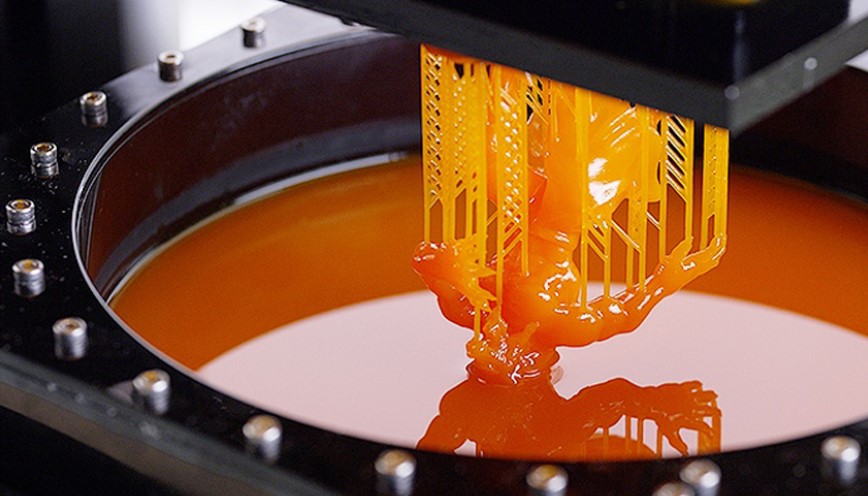
Stereolithography, also known as vat photopolymerization or resin 3D printing, is an additive manufacturing process where a light source cures liquid resin into hardened plastic. SLA 3D printers use light to cure light-reactive thermoset materials called “resin.” When these resins are exposed to certain wavelengths of light, short molecular chains join together, polymerizing monomers and oligomers into solidified rigid or flexible geometries.
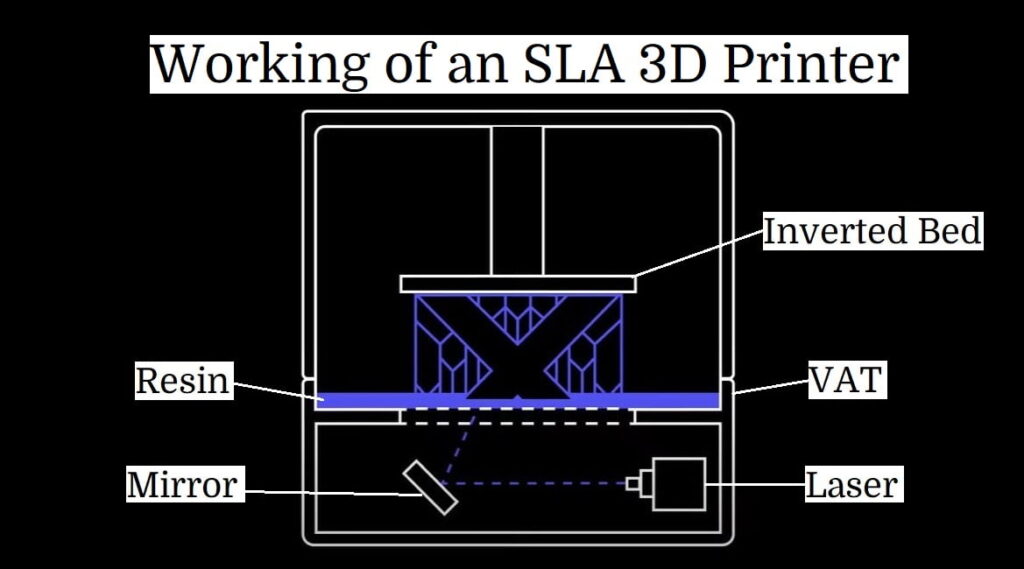
How Does SLA 3D Printing Work?
The SLA 3D printing process can be broken down into several key steps:
- Preparation:
The build platform is first positioned in a tank of liquid photopolymer at a distance of one layer height from the surface of the liquid. - Layer Curing:
A UV laser selectively cures and solidifies the photopolymer resin to create the next layer of the part. - Photopolymerization:
During this process, the monomer carbon chains in the liquid resin are activated by the UV laser’s light, causing them to solidify and form strong, unbreakable bonds with each other. - Laser Focus:
The laser beam is directed along a predetermined path using a set of mirrors, known as galvos. The entire cross-sectional area of the model is scanned, resulting in a fully solid part. - Post-Processing:
After printing, the part is in a not-fully-cured state and often requires further post-processing under UV light to achieve high mechanical and thermal properties.
It’s important to note that the photopolymerization process is irreversible, meaning SLA parts cannot be reverted back to their liquid form. When heated, these parts will burn rather than melt, as they are made of thermoset polymers, unlike the thermoplastics used in other 3D printing technologies like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM).
Materials Used in SLA 3D Printing
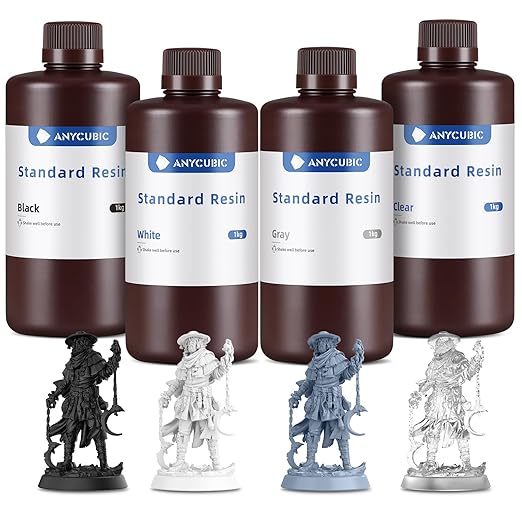
SLA 3D printing uses a range of materials known as photopolymers or resins. These are photo-reactive liquids that solidify when exposed to specific wavelengths of light. Each type of resin has its unique properties, making SLA a versatile technology for different applications. Below is a breakdown of the materials commonly used in SLA 3D printing:
- Standard Resins:
- These resins are widely used for producing parts with high resolution and fine details. They are ideal for prototypes and models but are generally brittle and less durable.
- Durable Resins (Polycarbonate-, Polypropylene-, ABS-like):
- These resins mimic the properties of durable plastics like polycarbonate, polypropylene, and ABS. They offer better strength and durability, though they may sacrifice some precision compared to standard resins.
- Flexible Resins:
- Flexible resins produce parts that can bend and stretch, making them suitable for applications requiring elasticity, such as custom-fit wearables or soft-touch components.
- Tough Resins:
- Tough resins are designed to withstand mechanical stress and strain, making them ideal for functional prototypes and parts that need to endure repetitive use.
- Clear Resins:
- Clear resins allow for the creation of parts with a glass-like transparency, suitable for applications where light transmission or aesthetic clarity is essential.
- High-Temperature Resins:
- These resins can withstand elevated temperatures, making them suitable for creating molds, casting patterns, or functional parts that will be exposed to heat.
- Castable Resins:
- Castable resins are used primarily in jewelry and dental industries. They can be burned out cleanly, leaving no residue, which is ideal for investment casting.
- Medical-Grade Resins:
- Medical-grade resins are biocompatible and sterilizable, making them suitable for producing surgical guides, dental aligners, and other medical devices.
- Filled Resins (Metal or Ceramic-Filled):
- Filled resins contain metal or ceramic particles, creating parts with enhanced thermal or mechanical properties. These parts, known as “green” parts, typically require heat treatment after printing to achieve their final properties.