How Will 3D Printing Shape the Future of Manufacturing?
The world of manufacturing has always been shaped by technological advancements, from the Industrial Revolution to the rise of automation. But one of the most transformative innovations in recent decades is 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing. This technology has already begun to reshape industries, from automotive and aerospace to healthcare and consumer goods. As 3D printing continues to evolve, its impact on manufacturing is set to become even more profound. This blog will explore how 3D printing will shape the future of manufacturing, the shifts we can expect from past to future, the growing demand, and predictions for its role in the industry.
From Past to Future: The Evolution of 3D Printing in Manufacturing
When 3D printing first emerged in the 1980s, it was primarily used for rapid prototyping. Manufacturers could quickly create models of new products without having to rely on traditional, time-consuming methods. This ability to build prototypes layer by layer using materials such as plastic and resin revolutionized the design process. However, early 3D printers were expensive, limited in the materials they could use, and slow compared to traditional manufacturing techniques like injection molding or CNC machining.
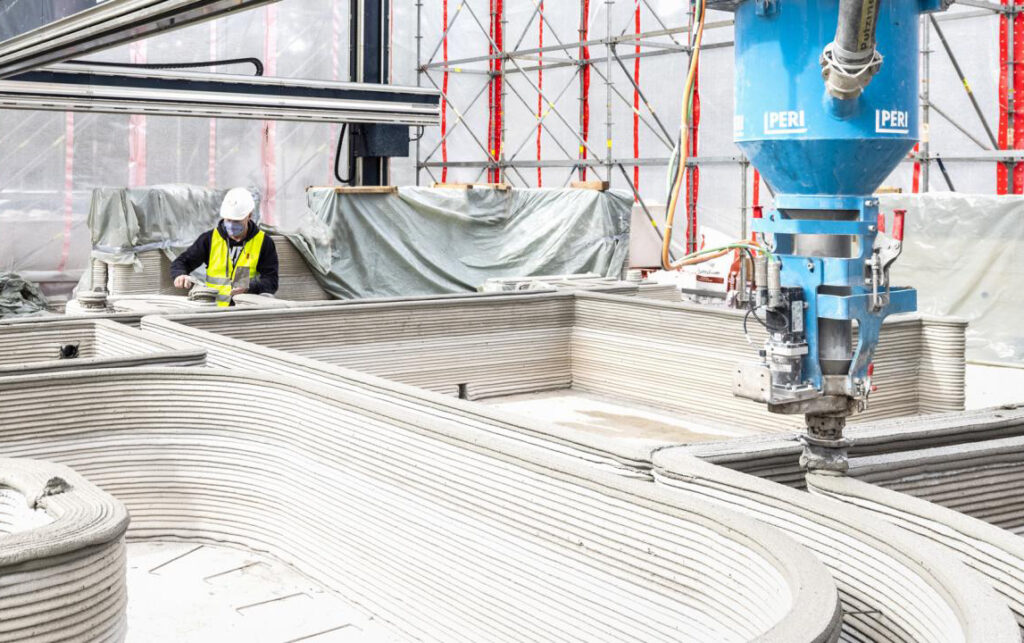
Fast forward to today, and the landscape has dramatically changed. Thanks to advances in materials science, 3D printing can now use metals, ceramics, and even bio-materials. The speed of printing has also improved, with some systems capable of producing functional parts in a matter of hours instead of days. The range of applications has expanded beyond prototyping to include end-use products, customized components, and even entire structures like houses.
Looking to the future, we can expect even greater advancements. New 3D printing technologies will enable faster production, more diverse material options, and greater integration with other manufacturing processes. For example, hybrid manufacturing that combines CNC machining with additive techniques will become more common, allowing manufacturers to leverage the strengths of both approaches.
Key Changes in Manufacturing Due to 3D Printing
Customization and Personalization: One of the most significant changes 3D printing will bring is the ability to mass-produce highly customized products. Traditional manufacturing relies on economies of scale, with large quantities of identical parts being produced to reduce costs. In contrast, 3D printing allows for customization without significant cost increases. This is already being seen in industries like healthcare, where customized medical implants and prosthetics are tailored to individual patients. In the future, consumers might order custom-fit shoes, glasses, or even cars that are produced on-demand, reducing the need for mass inventory and waste.
On-Demand Production: 3D printing also paves the way for on-demand manufacturing. Instead of maintaining large warehouses of parts and products, manufacturers could produce items as needed. This reduces inventory costs, minimizes waste, and shortens supply chains. In the future, distributed manufacturing centers equipped with 3D printers could fulfill orders locally, reducing transportation costs and carbon footprints. This model will also make manufacturing more resilient to disruptions, as companies will be able to quickly adapt to changes in demand or supply chain constraints.
Complex Designs Made Simple: Traditional manufacturing methods often have limitations when it comes to creating complex geometries. Parts with intricate internal structures or multiple moving components can be difficult or impossible to produce with techniques like casting or injection molding. 3D printing, however, builds objects layer by layer, making it possible to produce parts with complex designs in a single step. As a result, we could see more efficient designs, lighter parts, and innovations that were previously unimaginable due to manufacturing constraints.
Sustainability: The environmental impact of manufacturing is a growing concern, and 3D printing offers potential solutions. Traditional manufacturing methods often produce a lot of waste, whether from excess material used in cutting or shaping or from overproduction to meet minimum order quantities. 3D printing, by contrast, is an additive process, meaning material is only used where it’s needed. This reduces waste and can lead to more efficient resource use. Furthermore, 3D printing can incorporate recycled materials, reducing the demand for raw resources. As sustainability becomes a top priority for industries worldwide, 3D printing will likely play a critical role in creating more environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
Decentralized Manufacturing: In the future, we might see a shift toward decentralized manufacturing models, where production is spread out across multiple smaller facilities equipped with 3D printers, rather than concentrated in a few large factories. This could allow businesses to be more agile and responsive to local market demands. It could also reduce transportation costs and emissions, as products could be produced closer to where they are needed. In the long term, decentralized manufacturing could become a key component of a more resilient and adaptable global supply chain.
The Growing Demand for 3D Printing in Manufacturing
The demand for 3D printing in manufacturing has been steadily increasing, and this trend is expected to accelerate. According to market research, the global 3D printing market is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by advances in technology and expanding applications across industries. The aerospace, automotive, and healthcare sectors are already embracing 3D printing for its ability to produce lightweight, durable, and highly customized components.
In the automotive industry, for instance, 3D printing is used to create lightweight parts that improve fuel efficiency and performance. In aerospace, companies like Boeing and Airbus are already using 3D-printed components in their aircraft. The medical field has also seen significant growth in the use of 3D printing for everything from prosthetics to surgical tools and even bioprinted tissues. As these applications continue to expand, the demand for 3D printing will only increase.
Predictions for 3D Printing’s Role in Manufacturing
Increased Adoption Across Industries: While 3D printing is already making waves in certain sectors, we can expect to see it adopted more widely across other industries in the coming years. Consumer goods, electronics, fashion, and even food production could all benefit from 3D printing’s ability to create complex, customized products quickly and efficiently.
Continued Innovation in Materials: The development of new materials will be critical to the future success of 3D printing. While plastics and metals are currently the most commonly used materials, we are beginning to see the emergence of new options like biocompatible materials for medical applications and sustainable materials made from recycled or renewable sources. In the future, advanced materials that offer superior performance, such as carbon composites or graphene, could open up new possibilities for 3D printing in high-performance applications.
Cost Reduction and Accessibility: As the technology continues to evolve and become more widespread, the costs associated with 3D printing are likely to decrease. This will make it more accessible to smaller businesses and startups, enabling more companies to take advantage of its benefits. Affordable desktop 3D printers are already available, allowing individuals and small businesses to produce prototypes and small-batch products in-house. In the future, we could see 3D printing democratize manufacturing, making it possible for entrepreneurs and innovators to create products without the need for large-scale production facilities.
Integration with Smart Manufacturing: 3D printing will likely become an integral part of the broader trend toward smart manufacturing, which involves the use of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to optimize production processes. By integrating 3D printing with smart manufacturing systems, companies will be able to monitor and control every aspect of production in real time, leading to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and higher-quality products.
How 3D Printing Will Affect the Manufacturing Industry
The impact of 3D printing on the manufacturing industry will be profound. As more companies adopt this technology, we will see shifts in how products are designed, produced, and distributed. Traditional mass-production methods will be complemented, and in some cases replaced, by more flexible, decentralized manufacturing models. Businesses will be able to offer more personalized products to consumers, while also reducing waste and improving sustainability.
Moreover, 3D printing will enable innovation in product design and materials that were previously impossible. Manufacturers will be able to create parts with complex geometries, lightweight structures, and integrated functions in a way that was not feasible with traditional methods. This will lead to new product categories and the evolution of industries that are not yet fully utilizing the potential of 3D printing.
In the long term, the adoption of 3D printing will likely lead to significant changes in the labor market. While some traditional manufacturing jobs may be displaced, there will be a growing demand for skilled workers who can operate and maintain 3D printing systems, as well as those who can design and optimize products for additive manufacturing.